Wind
Heather Broman
Energy Storage
Accure Battery Intelligence
Wind
Dr. Sandeep Gupta

Submissions for the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO) American-Made Solar Photo Competition: Hit Me with Your Sun Shot are due May 23 at 5 p.m. ET. If you haven’t already submitted your photos, now is the time to do so!

Winners can earn up to $2,500 for a photo in one of eight categories:
SETO will feature winning entries on its website, at solar events and conferences, and in other outreach materials.
All professional and amateur photographers are encouraged to enter the competition. Photos submitted must be taken in the United States or U.S. territories and be an original work of the person submitting.
View the official rules for the competition, watch American-Made's informational webinar, and submit your photos today. We look forward to reviewing your best sun shots!
Solar Energy Technologies Office | energy.gov/eere

In honor of this year's Earth Day, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced the launch of the $7 billion Solar for All Grants program, awarding a total of 60 recipients across the nation. Among these, over $750 million has been allocated to Southeastern states, including Arkansas, Georgia, North Carolina, Florida, Tennessee, and South Carolina. The Southeast Sustainability Directors Network (SSDN) played a direct role in supporting grant awardees in Georgia and Arkansas, highlighting its dedication to advancing sustainable energy solutions and ensuring equitable access to solar resources across the Southeast.
SSDN played a pivotal role in supporting the Georgia BRIGHT Communities Coalition’s application, which was led by the Community Development Financial Institution Capital Good Fund in coalition with the cities of Savannah, Atlanta, and Decatur. The Coalition’s application secured a significant award of $156,010,000 and garnered recognition from the Biden-Harris administration for its recent success in residential engagement. SSDN provided grant narrative support and offered strategic policy guidance, contributing to the program's success in advancing renewable energy and community well-being. In addition to supporting the expansion of the BRIGHT leasing program, which launched in September of 2023, the coalition’s award will provide financing support to utilities to facilitate low-income-focused community solar programs, create a free “direct install” solar program for the most vulnerable households, and support “Community Benefit” solar projects at essential community facilities that agree to re-invest their realized savings in expanded services or other community benefits.
“This is a once-in-a-generation investment in equitable clean energy,” said Alicia Brown, Interim Director of Sustainability for the City of Savannah. “We are so thankful to the EPA for taking a chance on our community-centered vision and we look forward to getting these resources into communities who so desperately need lower energy bills, new economic opportunities, and increased resilience against outages.”
In Arkansas, SSDN provided funding to support the Arkansas Advanced Energy Association, led by Hope Enterprise Corporation, in developing its grant narrative. This collaboration has resulted in a significant award that will advance residential rooftop solar and storage, multi-family behind-the-meter solar projects, and financing for community solar initiatives.
"We are deeply appreciative of SSDN’s invaluable support, which was instrumental in enabling a final submission for this transformative opportunity,” said Lauren Waldrip of the Arkansas Advanced Energy Association. "With SSDN's assistance and the leadership of Hope Enterprise Corporation as the primary applicant, we are encouraged by the potential for this program to serve low-income Arkansans. The $93,670,000 grant award will play a pivotal role in expanding access to renewable energy through residential rooftop solar, multi-family behind-the-meter solar projects, and community solar financing initiatives across Arkansas.”
In addition to Solar For All grants directly supported by SSDN, they supported several state-wide efforts led by the South Carolina Office of Resilience (SCOR), Virginia Energy, North Carolina Clean Energy Fund (NCCEF), and the Florida SUN initiative, collecting letters of support from municipal and county member governments, promoting attendance at outreach events, and fostering community involvement in clean energy solutions.
SSDN is committed to advancing sustainability and promoting clean energy adoption in the Southeast region. Through strategic partnerships, SSDN continues to foster collaboration among stakeholders and empowers communities to embrace renewable energy solutions.
For more information about SSDN and its initiatives, including the Local Infrastructure Hub, please visit: www.southeastsdn.org/programs/ssdns-federal-programs/local-infrastructure-hub-cohorts/.
Southeast Sustainability Directors Network | https://www.southeastsdn.org/
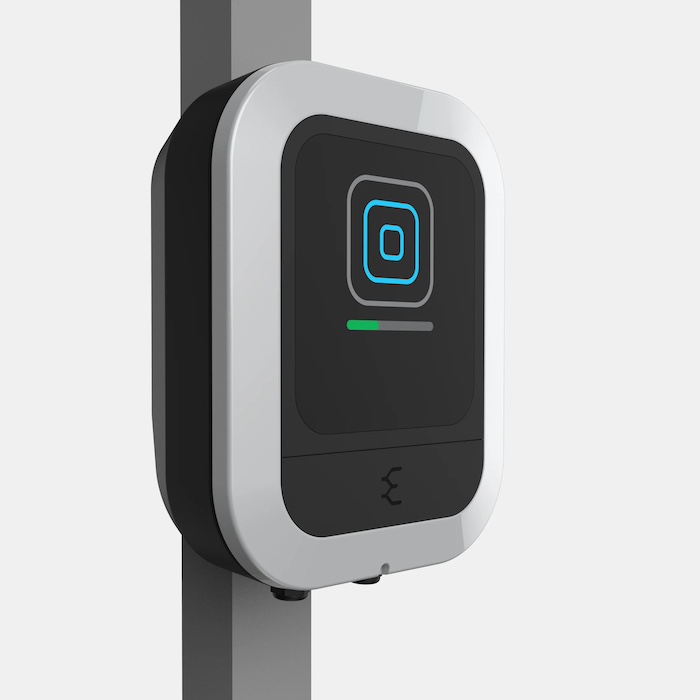

Enteligent Inc., developer of solar-powered electric vehicle service equipment (EVSE) and solar power optimization technologies, is accepting pre-orders for the world’s first solar-powered DC-to-DC charger, the Enteligent TLCEV T1 EVSE. This device provides convenient and affordable daytime charging directly from on-site solar generation, fostering a fundamental shift in energy consumption habits so solar power can be used to charge where it’s generated.
“If you’re charging your EV at night, you’re not using clean energy. Most EV owners plug in at night when peak demand is provided by fossil fuels.” said Enteligent co-founder and CEO Sean Burke. “Enteligent’s solution offers convenient EV charging so EV drivers can shift to daytime charging directly from solar panels and top-up for free while the sun shines. The TLCEV chargers simply connect to a solar canopy anywhere and generate clean power.”
Powered directly from the sun, the TLCEV T1 charger’s convenient design can easily integrate EV charging into solar canopies and carports located at residences, office parking lots, campuses, agricultural locales, and construction sites. Since the chargers do not rely on the grid, they do not require lengthy permitting processes and avoid complicated grid integration.
The direct DC-coupled charging provides NACS & CCS-1 options for consumers, making clean solar widely accessible.
Enteligent’s TLCEV chargers can supply up to 12.5 kW of fast DC charging – two times faster than many AC Level 2 EV chargers. The TLCEV T1 12.5 kW DC Charger also eliminates the DC-to-AC-to-DC conversion losses, resulting in up to 20% energy savings.
Pre-orders for TCLEV T1 EV charger are now being accepted HERE.
Enteligent | https://enteligent.com/

ONYX Insight, a leading global predictive analytics solution provider, has continued its growth in Asia Pacific after securing its first contract in Indonesia.
Following a successful field trial, the contract will see ONYX deliver its ecoCMS and fleetMONITOR technology to 30 turbines across UPC Renewables’ Sidrap farm, providing comprehensive data and analysis to enable long-term predictive maintenance (PdM) strategies.

The 75 MW Sidrap onshore wind farm is Indonesia’s first utility-scale wind farm and began providing power to the Southern PLN grid in 2018.
The application of ONYX’s technology supports PdM strategies by allowing operators to effectively manage and plan turbine inspection and maintenance requirements for key components, including drivetrains, pitch bearings and blades. This approach to condition monitoring creates significant cost and time efficiencies while enhancing safety.
The company’s ecoCMS provides advanced sensing and hardware to deliver reliable, high-quality data which allows operators to accurately understand asset health. The technology is easily integrated with third-party systems to deliver a cost-effective condition monitoring system (CMS) for legacy turbines through to modern multi-megawatt machines.
The ecoCMS data will be analysed in fleetMONITOR by ONYX’s monitoring engineers, enabling detailed insights from vibration, temperature, particle counters, and lubrication data. The condition monitoring solution will diagnose reliability problems for UPC Renewables turbine components up to 24 months before they become critical and enable the operator to plan with confidence, maximising performance and minimising cost.
UPC Renewables engaged with ONYX after experiencing issues with its legacy condition monitoring systems (CMS) detecting main bearing failures. It was vital that ecoCMS could establish a data connection with the incumbent oil particle counter, which was confirmed during the trial. With ONYX’s technology installed, all turbine data is consolidated in one place, delivering a single source of information for turbine health.
Bruce Hall, ONYX Insight CEO said: “This contract is a key milestone for ONYX as we enter the Indonesian market and strengthen our footprint across Asia Pacific. The region is leading the market with a high volume of installed capacity expected in the coming years and our predictive maintenance solutions can deliver tangible benefits, particularly with early adoption, by enabling operators to plan and execute maintenance before it becomes critical.
“As the world continues to rely more heavily on renewable energy and new wind farms come online, its essential that turbines operate at a maximum capacity and tackling reliability issues is high on the wind sector’s agenda. The cost of component replacement is substantial and if the turbine is offshore, these costs increase significantly. Proven technology such as our ecoCMS and fleetMONITOR allows operators to effectively reduce O&M spend while increasing productivity at a time when it has never been more important.”
ONYX Insight | https://onyxinsight.com/
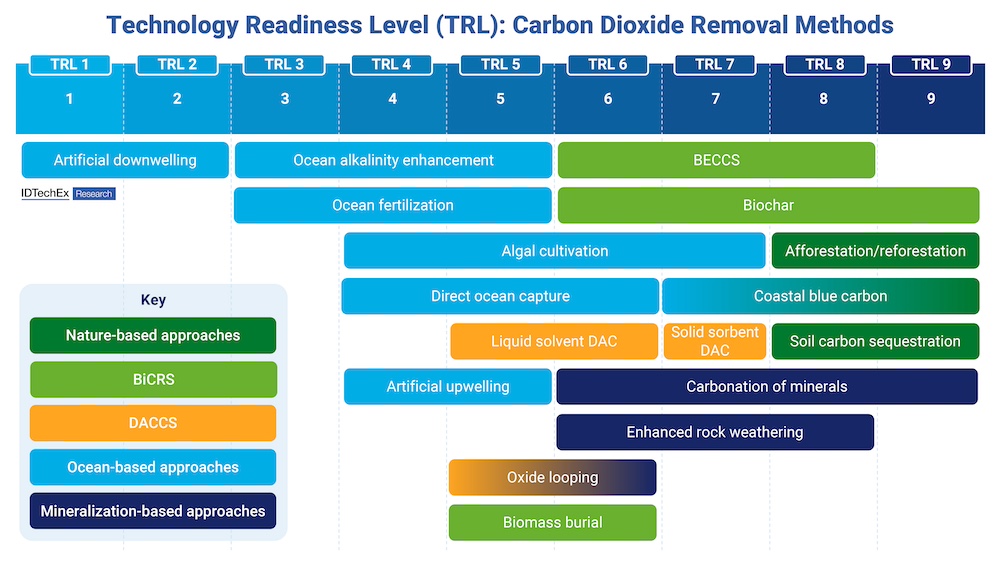
Carbon dioxide removal (CDR) will be needed to reach any international net zero emission targets and avoid global warming beyond 1.5-2°C. Negative emissions technologies (NETs), especially those that go beyond nature-based approaches to provide long-lasting scalable CO2 removals, have therefore been receiving increased support through government policy and voluntary carbon credit purchases from corporations with ambitious climate goals. IDTechEx predicts that by 2044, the world's capacity for such durable, engineered CO2 removals will exceed 630 megatonnes per annum.
The new IDTechEx report, "Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) 2024-2044: Carbon Credit Markets, Technologies, Players, and Forecasts", provides a comprehensive outlook of the emerging CDR industry and carbon credit markets, with an in-depth analysis of the technological, economic, regulatory, and environmental aspects that are shaping this market. In it, IDTechEx focuses on technologies that actively draw CO₂ from the atmosphere and sequester it into carbon sinks, namely:
1. Direct air carbon capture and storage (DACCS), which leverages chemical processes to capture CO₂ directly from the air and sequester it in geologic formations or durable products.
2. Biomass with carbon removal and storage (BiCRS), which involves strategies that use biomass to remove CO2 from the atmosphere and store it underground or in long-lived products. It includes approaches such as BECCS (bioenergy with carbon capture and storage), biochar, biomass burial, and bio-oil underground injection.
3. Nature-based CDR methods that leverage biological processes to increase carbon stocks in soils, forests, and other terrestrial ecosystems, i.e., afforestation/reforestation and soil carbon sequestration techniques.
4. Mineralization NETs that enhance natural mineral processes that permanently bind CO₂ from the atmosphere with rocks through enhanced rock weathering, carbonation of mineral wastes, and oxide looping.
5. Ocean-based CDR methods that strengthen the ocean carbon pump through ocean alkalinity enhancement, direct ocean capture, artificial upwelling/downwelling, coastal blue carbon, algae cultivation/marine seaweed sinking, and ocean fertilization.
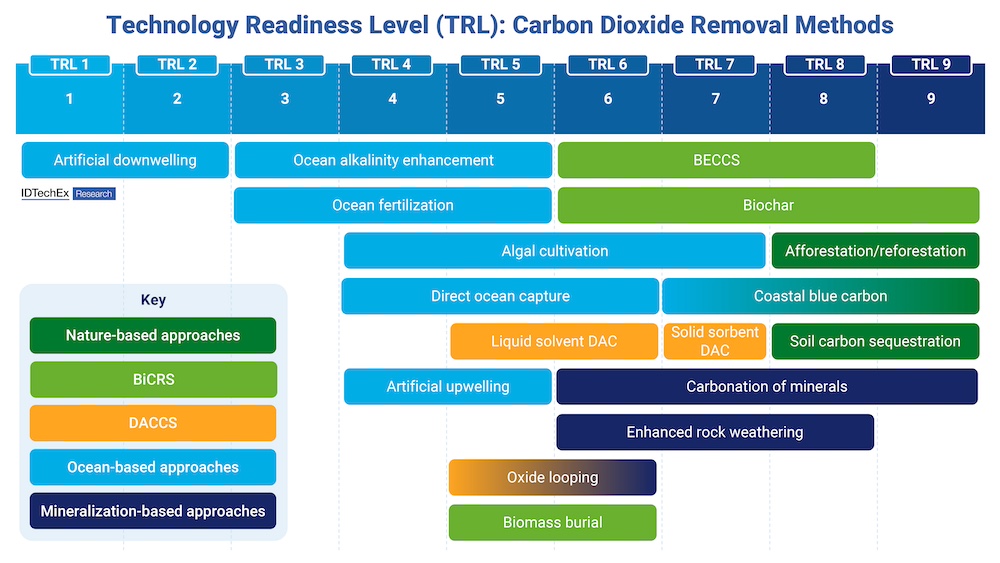
TRL (technology readiness level) chart of carbon dioxide removal technologies covered in the IDTechEx report. Source: IDTechEx
These CDR technologies are at vastly different stages of readiness. Some are nearly ready for large-scale deployment, while others require basic scientific research and further field trials.
Durable, engineered removals versus nature-based CDR solutions
Afforestation/reforestation solutions have historically dominated the supply of CDR due to their low cost and high maturity. However, demand for this type of removal carbon credit has been dropping in voluntary markets over the past few years due to several high-profile scandals and the low durability/permanence associated with nature-based CDR. Instead, corporate buyers have increasingly turned towards highly durable, engineered carbon removal credits generated from approaches such as DACCS and BECCS. These removals offer credible climate action but have a high price tag and are in short supply. Most durable engineered approaches are yet to be included in compliance markets and, therefore, rely on pre-purchases from corporate buyers for early-stage commercial development.
The new IDTechEx report, "Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) 2024-2044: Carbon Credit Markets, Technologies, Players, and Forecasts", provides insights into the most promising technologies being developed in CDR, highlighting the pros and cons of each method, examining key drivers and barriers for growth, and comparing the removal potential, capture cost, and durability of all technologies. Despite capacity currently being limited, there has been much interest in DACCS as a solution to permanently remove CO₂ from the atmosphere and reverse climate change. DACCS is immediate, measurable, allows for permanent storage, can be located practically anywhere, is likely to cause minimal ecosystem impacts, and can achieve large-scale removals.
However, the rate at which DACCS can be scaled up is likely a limiting factor. The challenges of deploying DACCS include the large energy inputs (requiring substantial low-carbon energy resources), the high cost, and the sorbent requirements. The industry is aiming for the ambitious target of gigatonne-scale of DACCS removals by 2050. To make this happen, corporate action, investments, policy shapers, and regulatory guidelines need to come together to bring down the costs.
Although BECCS is currently the most mature and widely deployed durable engineered CDR technology, scale-up has historically been slow, and planned capacity is modest. Despite the technologies behind BECCS being relatively mature, there is a risk that using biomass for CO₂ removal and storage may compete with agricultural land and water or negatively impact biodiversity and conservation. IDTechEx analysis has indicated that BECCS has a large potential to contribute to climate change mitigation, though not at the scale assumed in some models due to economic and environmental risk factors.
Comprehensive analysis and market forecasts
IDTechEx's "Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) 2024-2044: Carbon Credit Markets, Technologies, Players, and Forecasts" report assesses the CDR carbon credit market in detail, evaluating the different technologies, latest advancements, and potential adoption drivers and barriers. The report also includes a granular forecast until 2044 for the deployment of nine NET categories (DACCS, BECCS, biochar, biomass burial, direct ocean capture, ocean alkalinity enhancement, seaweed sinking, enhanced rock weathering, and carbonation of minerals) alongside exclusive analysis and interview-based company profiles.
Some of the key questions answered in this report:
• What are the requirements (energy, land, water, feedstocks, supply chain) for the deployment of CDR methods?
• What is the climate impact of implementing CDR on a large scale?
• Which gaps (technological, regulatory, business model) need to be addressed to enable each NET?
• What is the status of CDR within compliance markets and voluntary carbon credit markets, and what is the market potential?
• What are the key drivers and hurdles for CDR market growth?
• How much do CDR solutions cost today and may cost in the future?
• Who are the key players in the CDR space?
• What is needed to further develop the CDR sector?
To find out more about this report, including downloadable sample pages, please visit www.IDTechEx.com/CDR.
For the full portfolio of energy and decarbonization market research from IDTechEx, please see www.IDTechEx.com/Research/Energy.
Upcoming free-to-attend webinar
Carbon Credit Markets: The Rise of Durable, Engineered, Carbon Dioxide Removal Technologies
Eve Pope, Technology Analyst at IDTechEx and author of this article, will be presenting a free-to-attend webinar on the topic on Wednesday 5 June 2024 - Carbon Credit Markets: The Rise of Durable, Engineered, Carbon Dioxide Removal Technologies.
This webinar will reveal insights into the CDR space, and its content includes:
• Importance of carbon dioxide removal in reaching global net-zero emissions targets.
• Overview of all negative emission technologies (NETs): Direct air carbon capture and storage (DACCS), Biomass with carbon removal and storage (BiCRS), Nature-based CDR methods, Mineralization NETs, and ocean-based CDR approaches
• Contextualization of CDR within carbon markets and how voluntary carbon credits are accelerating NETs in the short-term
• Identifying the key factors driving the market pivot from nature-based solutions such as afforestation/reforestation to durable, engineered, CDR approaches
• Discussion of environmental, technical, and economic drivers/barriers for DACCS and BECCS
Please click here to check timings and register for your specific time zone.
If you are unable to make the date, please register anyway to receive the links to the on-demand recording (available for a limited time) and webinar slides as soon as they are available.
IDTechEx | www.idtechex.com

COP28 President Dr. Sultan Al Jaber officially tasked the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) with the establishment of a special annual report series dedicated to monitoring progress and providing recommendations on achieving key energy goals of the UAE Consensus set at COP28.
The call to triple renewable power capacity and double energy efficiency by 2030 reflects vital components of the global response to address climate change and keep 1.5°C within reach. The UAE Consensus calls for 'transitioning away from fossil fuels in energy systems, in a just, orderly and equitable manner' with the aim to achieve net zero by 2050.
COP28 President Dr Sultan Al Jaber said, “Tripling renewable energy capacity and doubling energy efficiency by 2030 are central parts of the UAE Consensus, agreed by all 198 Parties at COP28. IRENA’s annual report will track and monitor global progress against these targets, which are crucial in ensuring we turn agreement into action and keep 1.5°C within reach. The energy transition offers the greatest opportunity for social and economic development since the industrial revolution, and in IRENA we have a partner who understands both the need to transition to renewable energy and the huge economic opportunity this offers.”
IRENA Director-General Francesco La Camera welcomed the recognition of IRENA’s new custodian role: “I confirm the unwavering commitment by IRENA to the successful implementation of the historic UAE Consensus. Given the centrality of the Agency’s World Energy Transitions Outlook 1.5°C Pathway to the tripling of renewables and doubling of energy efficiency goals, IRENA is best placed to monitor progress towards these vital outcomes and ensure commitments are transformed into firm action and progress on the ground.”
The new annual tracking report, which will be led, developed and published by IRENA, as official Custodian Agency, each year from 2024 to 2030, will feature the latest data and projections concerning the tripling of renewables and doubling of energy efficiency by 2030, providing timely and accurate inputs to future COP engagements.
IRENA | www.irena.org

Clarios, a global leader in advanced battery solutions and Altris, a Swedish developer and prototype manufacturer of sodium-ion batteries, announced an exclusive Joint Development Agreement (JDA) for low voltage mobility applications.
Under the new JDA, Altris will focus on developing the sodium ion cell technology for low-voltage applications, while Clarios will leverage its expertise in Battery Management Systems (BMS), software, and system integration to design the battery system. This development agreement enhances a collaboration agreement initiated earlier this year, which set in motion the creation of a detailed production plan for low-voltage vehicle batteries utilizing sodium-ion cells. This initiative is particularly timely, aligning with a pivotal moment in the global automotive industry’s transformation.
Every vehicle, including hybrid and fully electric models, requires a reliable low-voltage energy source to power essential systems and functions. As the complexity of vehicles increases, the low-voltage network must adapt to support a growing array of software-based functions, including steer-by-wire, brake-by-wire, autonomous technologies, and enhanced in-cabin experiences. Sodium-ion (Na-ion) batteries are well suited to meet these increased power demand and at the same time are inherently sustainable and easy to recycle. Na-ion technology offers an energy density on par with LFP battery technologies and is particularly sustainable thanks to its environmentally friendly and easily recyclable materials. The materials used to produce Na-ion cells – salt, wood, iron and air – are abundant and free from conflict minerals and toxic elements. Developing Na-ion batteries for vehicles would represent an important advancement in automotive battery technology and advance the circularity goals of the automotive industry.
“This Joint Development Agreement with Altris enables Clarios to further expand our leading position in the development of innovative battery solutions and to meet the growing demand for sustainable energy storage systems. This is a significant step forward with our strategy of being chemistry-agnostic when it comes to producing low-voltage batteries,” said Federico Morales Zimmermann, Clarios vice president and General Manager, Global Customers, Products and Engineering. “We now have the ability to manufacture a variety of advanced battery types including absorbent glass mat, lithium-ion and Na-ion to support the low-voltage demands created by advanced vehicle technologies.”
“Altris wants to bring the world better, safer and truly sustainable sodium-ion batteries. This Joint Development Agreement with Clarios enables us to continue our focus on developing and manufacturing sodium-ion batteries specifically adapted for the automotive battery market. Our chemistry has a unique advantage of combining low-temperature performance with the ability of delivering high currents, all while maintaining a competitive energy density. This makes it a perfect fit for mobility solutions”, says Björn Mårlid, CEO of Altris.
The financial terms of the agreement were not disclosed by the companies
Altris | https://www.altris.se/
Clarios | https://www.clarios.com/

Alternative Energies May 15, 2023
The United States is slow to anger, but relentlessly seeks victory once it enters a struggle, throwing all its resources into the conflict. “When we go to war, we should have a purpose that our people understand and support,” as former Secretary ....

Unleashing trillions of dollars for a resilient energy future is within our grasp — if we can successfully navigate investment risk and project uncertainties.
The money is there — so where are the projects?
A cleaner and more secure energy future will depend on tapping trillions of dollars of capital. The need to mobilize money and markets to enable the energy transition was one of the key findings of one of the largest studies ever conducted among the global energy sector C-suite. This will mean finding ways to reduce the barriers and uncertainties that prevent money from flowing into the projects and technologies that will transform the energy system. It will also mean fostering greater collaboration and alignment among key players in the energy space.
 Interestingly, the study found that insufficient access to finance was not considered the primary cause of the current global energy crisis. In fact, capital was seen to be available — but not being unlocked. Why is that? The answer lies in the differing risk profiles of energy transition investments around the world. These risks manifest in multiple ways, including uncertainties relating to project planning, public education, stakeholder engagement, permitting, approvals, policy at national and local levels, funding and incentives, technology availability, and supply chains.
Interestingly, the study found that insufficient access to finance was not considered the primary cause of the current global energy crisis. In fact, capital was seen to be available — but not being unlocked. Why is that? The answer lies in the differing risk profiles of energy transition investments around the world. These risks manifest in multiple ways, including uncertainties relating to project planning, public education, stakeholder engagement, permitting, approvals, policy at national and local levels, funding and incentives, technology availability, and supply chains.
These risks need to be addressed to create more appealing investment opportunities for both public and private sector funders. This will require smart policy and regulatory frameworks that drive returns from long-term investment into energy infrastructure. It will also require investors to recognize that resilient energy infrastructure is more than an ESG play — it is a smart investment in the context of doing business in the 21st century.
Make de-risking investment profiles a number one priority
According to the study, 80 percent of respondents believe the lack of capital being deployed to accelerate the transition is the primary barrier to building the infrastructure required to improve energy security. At the same time, investors are looking for opportunities to invest in infrastructure that meets ESG and sustainability criteria. This suggests an imbalance between the supply and demand of capital for energy transition projects.
How can we close the gap?
One way is to link investors directly to energy companies. Not only would this enable true collaboration and non-traditional partnerships, but it would change the way project financing is conceived and structured — ultimately aiding in potentially satisfying the risk appetite of latent but hugely influential investors, such as pension funds. The current mismatch of investor appetite and investable projects reveals a need for improving risk profiles, as well as a mindset shift towards how we bring investment and developer stakeholders together for mutual benefit. The circular dilemma remains: one sector is looking for capital to undertake projects within their skill to deploy, while another sector wonders where the investable projects are.
This conflict is being played out around the world; promising project announcements are made, only to be followed by slow progress (or no action at all). This inertia results when risks are compounded and poorly understood. To encourage collaboration between project developers and investors with an ESG focus, more attractive investment opportunities can be created by pulling several levers: public and private investment strategies, green bonds and other sustainable finance instruments, and innovative financing models such as impact investing.

Expedite permitting to speed the adoption of new technologies
Another effective strategy to de-risk investment profiles is found in leveraging new technologies and approaches that reduce costs, increase efficiency, and enhance the reliability of energy supply. Research shows that 62 percent of respondents indicated a moderate or significant increase in investment in new and transitional technologies respectively, highlighting the growing interest in innovative solutions to drive the energy transition forward.
Hydrogen, carbon capture and storage, large-scale energy storage, and smart grids are some of the emerging technologies identified by survey respondents as having the greatest potential to transform the energy system and create new investment opportunities. However, these technologies face challenges such as long lag times between conception and implementation.
If the regulatory environment makes sense, then policy uncertainty is reduced, and the all-important permitting pathways are well understood and can be navigated. Currently, the lack of clear, timely, and fit-for-purpose permitting is a major roadblock to the energy transition. To truly unleash the potential of transitional technologies requires the acceleration of regulatory systems that better respond to the nuance and complexity of such technologies (rather than the current one-size-fits all approach). In addition, permitting processes must also be expedited to dramatically decrease the period between innovation, commercialization, and implementation. One of the key elements of faster permitting is effective consultation with stakeholders and engagement with communities where these projects will be housed for decades. This is a highly complex area that requires both technical and communication skills.
The power of collaboration, consistency, and systems thinking
The report also reveals the need for greater collaboration among companies in the energy space to build a more resilient system. The report shows that, in achieving net zero, there is a near-equal split between those increasing investment (47 percent of respondents), and those decreasing investment (39 percent of respondents). This illustrates the complexity and diversity of the system around the world. A more resilient system will require all its components – goals and actions – to be aligned towards a common outcome.
Another way to de-risk the energy transition is to establish consistent, transparent, and supportive policy frameworks that encourage investment and drive technological innovation. The energy transition depends on policy to guide its direction and speed by affecting how investors feel and how the markets behave. However, inconsistent or inadequate policy can also be a source of uncertainty and instability. For example, shifting political priorities, conflicting international standards, and the lack of market-based mechanisms can hinder the deployment of sustainable technologies, resulting in a reluctance to commit resources to long-term projects.

Variations in country-to-country deployment creates disparities in energy transition progress. For instance, the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act in the US has posed challenges for the rest of the world, by potentially channeling energy transition investment away from other markets and into the US. This highlights the need for a globally unified approach to energy policy that balances various national interests while addressing a global problem.
To facilitate the energy transition, it is imperative to establish stable, cohesive, and forward-looking policies that align with global goals and standards. By harmonizing international standards, and providing clear and consistent signals, governments and policymakers can generate investor confidence, helping to foster a robust energy ecosystem that propels the sector forward.
Furthermore, substantive and far-reaching discussions at international events like the United Nations Conference of the Parties (COP), are essential to facilitate this global alignment. These events provide an opportunity to de-risk the energy transition through consistent policy that enables countries to work together, ensuring that the global community can tackle the challenges and opportunities of the energy transition as a united front.
Keeping net-zero ambitions on track
Despite the challenges faced by the energy sector, the latest research reveals a key positive: 91 percent of energy leaders surveyed are working towards achieving net zero. This demonstrates a strong commitment to the transition and clear recognition of its importance. It also emphasizes the need to accelerate our efforts, streamline processes, and reduce barriers to realizing net-zero ambitions — and further underscores the need to de-risk energy transition investment by removing uncertainties.
The solution is collaborating and harmonizing our goals with the main players in the energy sector across the private and public sectors, while establishing consistent, transparent, and supportive policy frameworks that encourage investment and drive technological innovation.
These tasks, while daunting, are achievable. They require vision, leadership, and action from all stakeholders involved. By adopting a new mindset about how we participate in the energy system and what our obligations are, we can stimulate the rapid progress needed on the road to net zero.
Dr. Tej Gidda (Ph.D., M.Sc., BSc Eng) is an educator and engineer with over 20 years of experience in the energy and environmental fields. As GHD Global Leader – Future Energy, Tej is passionate about moving society along the path towards a future of secure, reliable, and affordable low-carbon energy. His focus is on helping public and private sector clients set and deliver on decarbonization goals in order to achieve long-lasting positive change for customers, communities, and the climate. Tej enjoys fostering the next generation of clean energy champions as an Adjunct Professor at the University of Waterloo Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering.
GHD | www.ghd.com
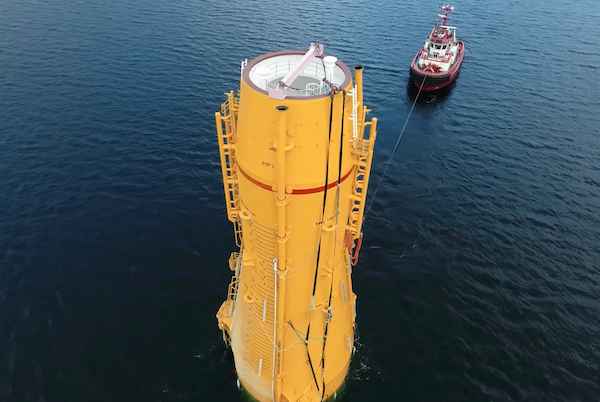

The Kincardine floating wind farm, located off the east coast of Scotland, was a landmark development: the first commercial-scale project of its kind in the UK sector. Therefore, it has been closely watched by the industry throughout its installation. With two of the turbines now having gone through heavy maintenance, it has also provided valuable lessons into the O&M processes of floating wind projects.
In late May, the second floating wind turbine from the five-turbine development arrived in the port of Massvlakte, Rotterdam, for maintenance. An Anchor Handling Tug Supply (AHTS)
vessel was used to deliver the KIN-02 turbine two weeks after a Platform Supply Vessel (PSV) and AHTS had worked to disconnect the turbine from the wind farm site. The towing vessel became the third vessel used in the operation.
This is not the first turbine disconnected from the site and towed for maintenance. In the summer of 2022, KIN-03 became the world’s first-ever floating wind turbine that required heavy maintenance (i.e. being disconnected and towed for repair). It was also towed from Scotland to Massvlakte.
Each of these operations has provided valuable lessons for the ever-watchful industry in how to navigate the complexities of heavy maintenance in floating wind as the market segment grows.
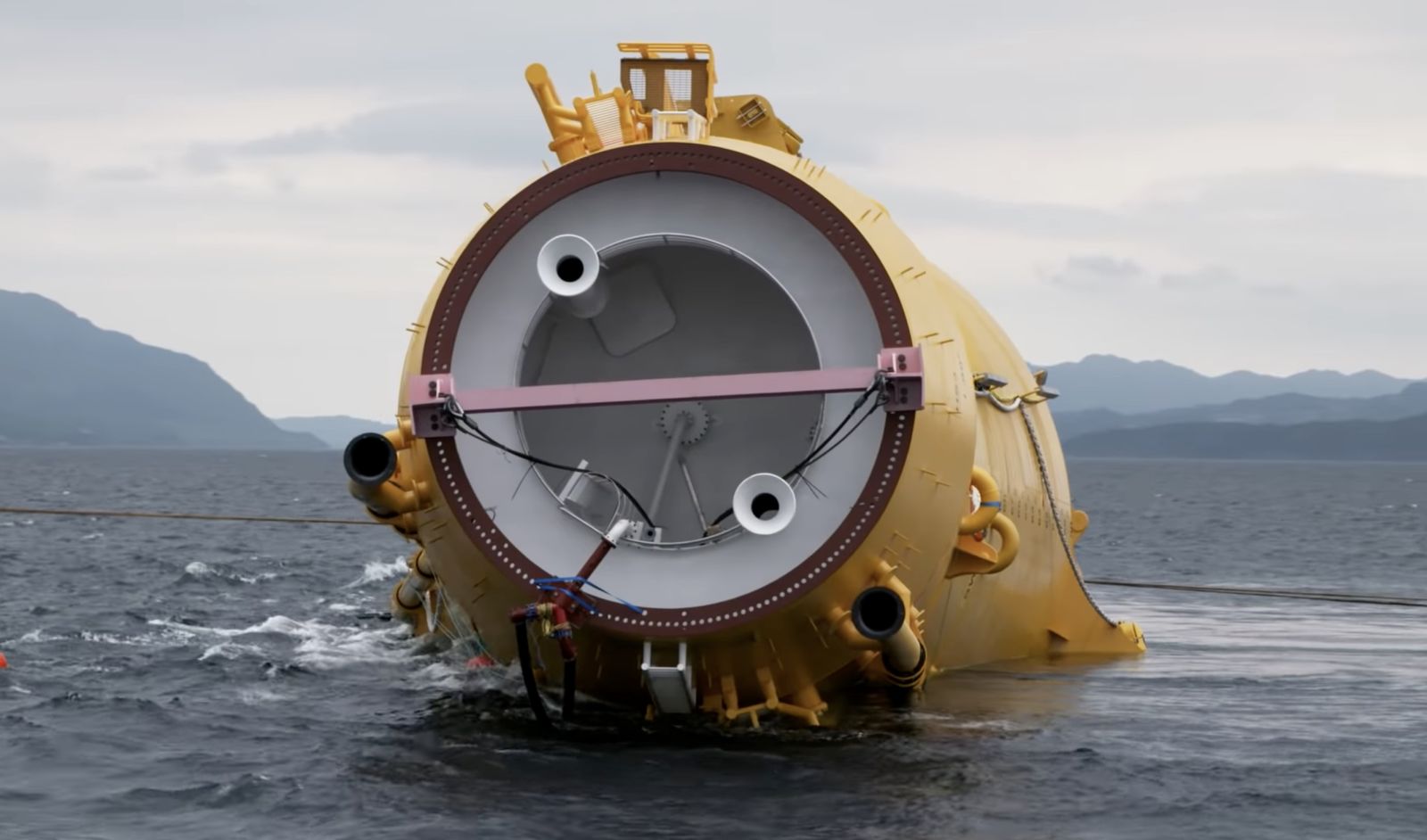

The heavy maintenance process
When one of Kincardine’s five floating 9.5 MW turbines (KIN-03) suffered a technical failure in May 2022, a major technical component needed to be replaced. The heavy maintenance strategy selected by the developer and the offshore contractors consisted in disconnecting and towing the turbine and its floater to Rotterdam for maintenance, followed by a return tow and re-connection. All of the infrastructure, such as crane and tower access, remained at the quay following the construction phase. (Note, the following analysis only covers KIN-03, as details of the second turbine operation are not yet available).
Comparing the net vessel days for both the maintenance and the installation campaigns at this project highlights how using a dedicated marine spread can positively impact operations.
For this first-ever operation, a total of 17.2 net vessel days were required during turbine reconnection—only a slight increase on the 14.6 net vessel days that were required for the first hook-up operation performed during the initial installation in 2021. However, it exceeds the average of eight net vessel days during installation. The marine spread used in the heavy maintenance operation differed from that used during installation. Due to this, it did not benefit from the learning curve and experience gained throughout the initial installation, which ultimately led to the lower average vessel days.
The array cable re-connection operation encountered a similar effect. The process was performed by one AHTS that spent 10 net vessel days on the operation. This compares to the installation campaign, where the array cable second-end pull-in lasted a maximum of 23.7 hours using a cable layer.
Overall, the turbine shutdown duration can be broken up as 14 days at the quay for maintenance, 52 days from turbine disconnection to turbine reconnection, and 94 days from disconnection to the end of post-reconnection activities.
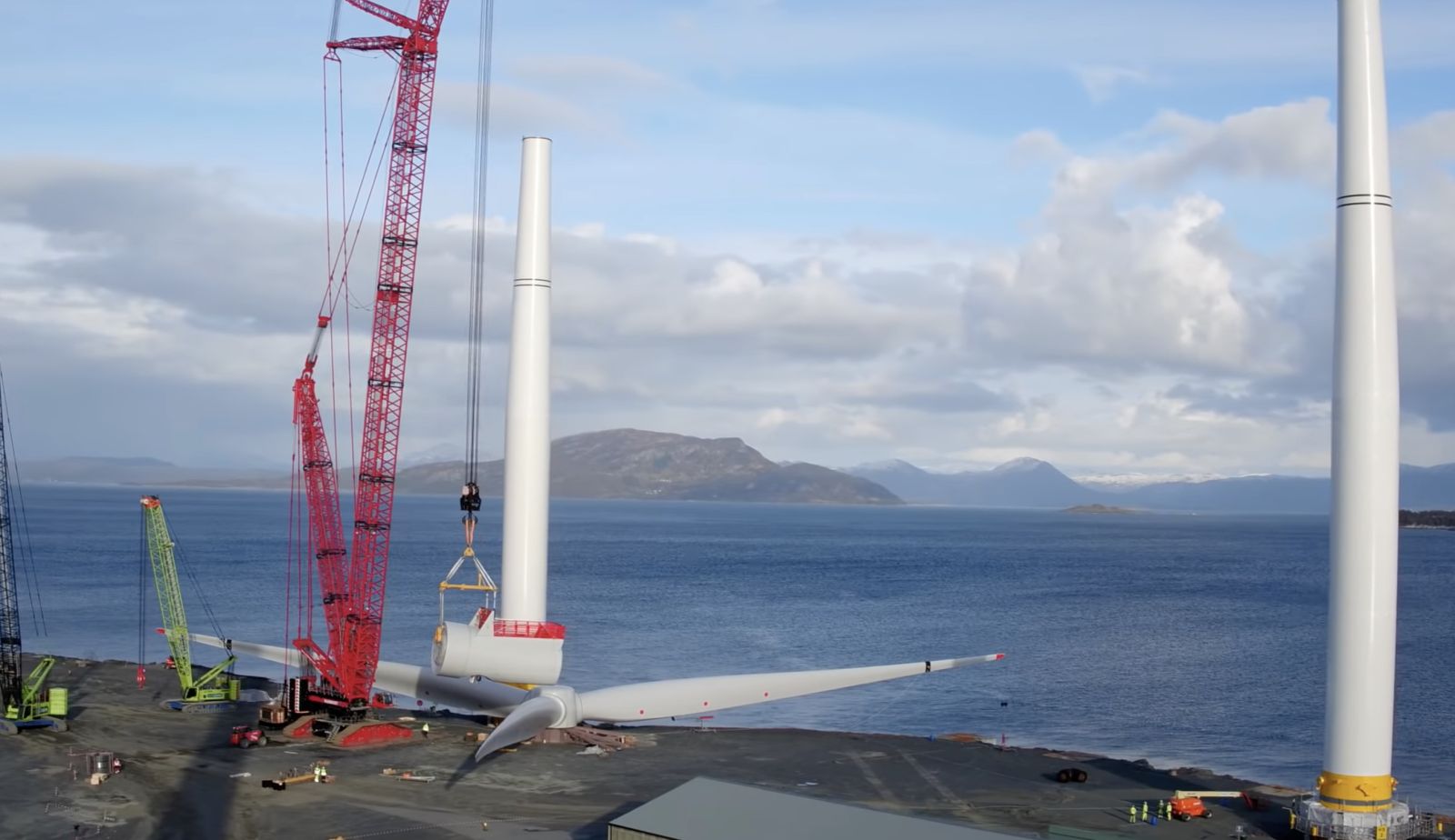

What developers should keep in mind for heavy maintenance operations
This analysis has uncovered two main lessons developers should consider when planning a floating wind project: the need to identify an appropriate O&M port, and to guarantee that a secure fleet is available.
Floating wind O&M operations require a port with both sufficient room and a deep-water quay. The port must also be equipped with a heavy crane with sufficient tip height to accommodate large floaters and reach turbine elevation. Distance to the wind farm should also be taken into account, as shorter distances will reduce towing time and, therefore, minimize transit and non-productive turbine time.
During the heavy maintenance period for KIN-03 and KIN-02, the selected quay (which had also been utilized in the initial installation phase of the wind farm project), was already busy as a marshalling area for other North Sea projects. This complicated the schedule significantly, as the availability of the quay and its facilities had to be navigated alongside these other projects. This highlights the importance of abundant quay availability both for installation (long-term planning) and maintenance that may be needed on short notice.
At the time of the first turbine’s maintenance program (June 2022), the North Sea AHTS market was in an exceptional situation: the largest bollard pull AHTS units contracted at over $200,000 a day, the highest rate in over a decade.
During this time, the spot market was close to selling out due to medium-term commitments, alongside the demand for high bollard pull vessels for the installation phase at a Norwegian floating wind farm project. The Norwegian project required the use of four AHTS above a 200t bollard pull. With spot rates ranging from $63,000 to $210,000 for the vessels contracted for Kincardine’s maintenance, the total cost of the marine spread used in the first repair campaign was more than $4 million.
Developers should therefore consider the need to structure maintenance contracts with AHTS companies, either through frame agreements or long-term charters, to decrease their exposure to spot market day rates as the market tightens in the future.
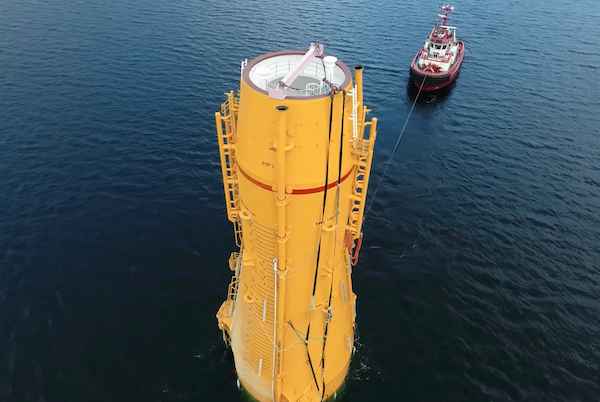

While these lessons are relevant for floating wind developers now, new players are looking towards alternative heavy O&M maintenance options for the future. Two crane concepts are especially relevant in this instance. The first method is for a crane to be included in the turbine nacelle to be able to directly lift the component which requires repair from the floater, as is currently seen on onshore turbines. This method is already employed in onshore turbines and could be applicable for offshore. The second method is self-elevating cranes with several such solutions already in development.
The heavy maintenance operations conducted on floating turbines at the Kincardine wind farm have provided invaluable insights for industry players, especially developers. The complex process of disconnecting and towing turbines for repairs highlights the need for meticulous planning and exploration of alternative maintenance strategies, some of which are already in the pipeline. As the industry evolves, careful consideration of ports, and securing fleet contracts, will be crucial in driving efficient and cost-effective O&M practices for the floating wind market.
Sarah McLean is Market Research Analyst at Spinergie, a maritime technology company specializing in emission, vessel performance, and operation optimization.
Spinergie | www.spinergie.com

According to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), developers plan to add 54.5 gigawatts (GW) of new utility-scale electric generating capacity to the U.S. power grid in 2023. More than half of this capacity will be solar. Wind power and battery storage are expected to account for roughly 11 percent and 17 percent, respectively.
A large percentage of new installations are being developed in areas that are prone to extreme weather events and natural disasters (e.g., Texas and California), including high wind, tornadoes, hail, flooding, earthquakes, wildfires, etc. With the frequency and severity of many of these events increasing, project developers, asset owners, and tax equity partners are under growing pressure to better understand and mitigate risk.
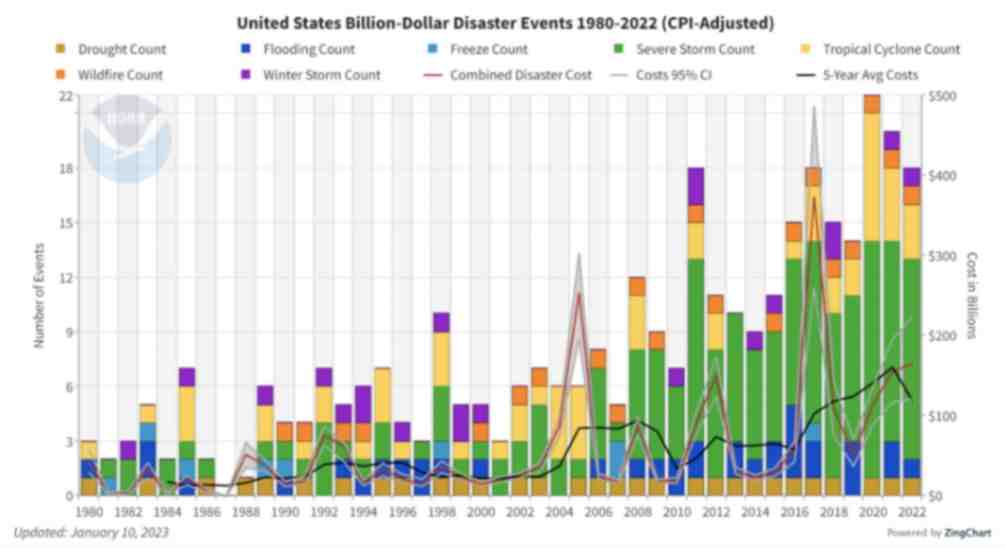
Figure 1. The history of billion-dollar disasters in the United States each year from 1980 to 2022 (source: NOAA)
In terms of loss prevention, a Catastrophe (CAT) Modeling Study is the first step to understanding the exposure and potential financial loss from natural hazards or extreme weather events. CAT studies form the foundation for wider risk management strategies, and have significant implications for insurance costs and coverage.
Despite their importance, developers often view these studies as little more than a formality required for project financing. As a result, they are often conducted late in the development cycle, typically after a site has been selected. However, a strong case can be made for engaging early with an independent third party to perform a more rigorous site-specific technical assessment. Doing so can provide several advantages over traditional assessments conducted by insurance brokerage affiliates, who may not possess the specialty expertise or technical understanding needed to properly apply models or interpret the results they generate. One notable advantage of early-stage catastrophe studies is to help ensure that the range of insurance costs, which can vary from year to year with market forces, are adequately incorporated into the project financial projections.
The evolving threat of natural disasters
Over the past decade, the financial impact of natural hazard events globally has been almost three trillion dollars. In the U.S. alone, the 10-year average annual cost of natural disaster events exceeding $1 billion increased more than fourfold between the 1980s ($18.4 billion) and the 2010s ($84.5 billion).

Investors, insurers, and financiers of renewable projects have taken notice of this trend, and are subsequently adapting their behavior and standards accordingly. In the solar market, for example, insurance premiums increased roughly four-fold from 2019 to 2021. The impetus for this increase can largely be traced back to a severe storm in Texas in 2019, which resulted in an $80 million loss on 13,000 solar panels that were damaged by hail.
The event awakened the industry to the hazards severe storms present, particularly when it comes to large-scale solar arrays. Since then, the impact of convective weather on existing and planned installations has been more thoroughly evaluated during the underwriting process. However, far less attention has been given to the potential for other natural disasters; events like floods and earthquakes have not yet resulted in large losses and/or claims on renewable projects (including wind farms). The extraordinary and widespread effect of the recent Canadian wildfires may alter this behavior moving forward.
A thorough assessment, starting with a CAT study, is key to quantifying the probability of their occurrence — and estimating potential losses — so that appropriate measures can be taken to mitigate risk.
All models are not created equal
Industrywide, certain misconceptions persist around the use of CAT models to estimate losses from an extreme weather event or natural disaster.

Often, the perception is that risk assessors only need a handful of model inputs to arrive at an accurate figure, with the geographic location being the most important variable. While it’s true that many practitioners running models will pre-specify certain project characteristics regardless of the asset’s design (for example, the use of steel moment frames without trackers for all solar arrays in a given region or state), failure to account for even minor details can lead to loss estimates that are off by multiple orders of magnitude.
The evaluation process has recently become even more complex with the addition of battery energy storage. Relative to standalone solar and wind farms, very little real-world experience and data on the impact of extreme weather events has been accrued on these large-scale storage installations. Such projects require an even greater level of granularity to help ensure that all risks are identified and addressed.
Even when the most advanced modeling software tools are used (which allow for thousands of lines of inputs), there is still a great deal that is subject to interpretation. If the practitioner does not possess the expertise or technical ability needed to understand the model, the margin for error can increase substantially. Ultimately, this can lead to overpaying for insurance. Worse, you may end up with a policy with insufficient coverage. In both cases, the profitability of the asset is impacted.
Supplementing CAT studies
In certain instances, it may be necessary to supplement CAT models with an even more detailed analysis of the individual property, equipment, policies, and procedures. In this way, an unbundled risk assessment can be developed that is tailored to the project. Supplemental information (site-specific wind speed studies and hydrological studies, structural assessment, flood maps, etc.) can be considered to adjust vulnerability models.
This provides an added layer of assurance that goes beyond the pre-defined asset descriptions in the software used by traditional studies or assessments. By leveraging expert elicitations, onsite investigations, and rigorous engineering-based methods, it is possible to discretely evaluate asset-specific components as part of the typical financial loss estimate study: this includes Normal Expected Loss (NEL), also known as Scenario Expected Loss (SEL); Probable Maximum Loss (PML), also known as Scenario Upper Loss (SUL); and Probabilistic Loss (PL).
Understanding the specific vulnerabilities and consequences can afford project stakeholders unique insights into quantifying and prioritizing risks, as well as identifying proper mitigation recommendations.
Every project is unique
The increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters and extreme weather events globally is placing an added burden on the renewable industry, especially when it comes to project risk assessment and mitigation. Insurers have signaled that insurance may no longer be the main basis for transferring risk; traditional risk management, as well as site and technology selection, must be considered by developers, purchasers, and financiers.
As one of the first steps in understanding exposure and the potential capital loss from a given event, CAT studies are becoming an increasingly important piece of the risk management puzzle. Developers should treat them as such by engaging early in the project lifecycle with an independent third-party practitioner with the specialty knowledge, tools, and expertise to properly interpret models and quantify risk.
Hazards and potential losses can vary significantly depending on the project design and the specific location. Every asset should be evaluated rigorously and thoroughly to minimize the margin for error, and maximize profitability over its life.
 Chris LeBoeuf is Global Head of the Extreme Loads and Structural Risk division of ABS Group, based in San Antonio, Texas. He leads a team of more than 60 engineers and scientists in the US, UK, and Singapore, specializing in management of risks to structures and equipment related to extreme loading events, including wind, flood, seismic and blast. Chris has more than 20 years of professional experience as an engineering consultant, and is a recognized expert in the study of blast effects and blast analysis, as well as design of buildings. He holds a Bachelor of Science in Civil Engineering from The University of Texas at San Antonio, and is a registered Professional Engineer in 12 states.
Chris LeBoeuf is Global Head of the Extreme Loads and Structural Risk division of ABS Group, based in San Antonio, Texas. He leads a team of more than 60 engineers and scientists in the US, UK, and Singapore, specializing in management of risks to structures and equipment related to extreme loading events, including wind, flood, seismic and blast. Chris has more than 20 years of professional experience as an engineering consultant, and is a recognized expert in the study of blast effects and blast analysis, as well as design of buildings. He holds a Bachelor of Science in Civil Engineering from The University of Texas at San Antonio, and is a registered Professional Engineer in 12 states.
ABS Group | www.abs-group.com

Throughout my life and career as a real estate developer in New York City, I’ve had many successes. In what is clearly one of my most unusual development projects in a long career filled with them, I initiated the building of a solar farm to help t....

I’m just going to say it, BIPV is dumb. Hear me out…. Solar is the most affordable form of energy that has ever existed on the planet, but only because the industry has been working towards it for the past 15 years. Governments,....

Heat waves encircled much of the earth last year, pushing temperatures to their highest in recorded history. The water around Florida was “hot-tub hot” — topping 101° and bleaching and killing coral in waters around the peninsula. Phoenix had ....

Wind turbines play a pivotal role in the global transition to sustainable energy sources. However, the harsh environmental conditions in which wind turbines operate, such as extreme temperatures, high humidity, and exposure to various contaminants, p....

Wind energy remains the leading non-hydro renewable technology, and one of the fastest-growing of all power generation technologies. The key to making wind even more competitive is maximizing energy production and efficiently maintaining the assets. ....

The allure of wind turbines is undeniable. For those fortunate enough to visit these engineering marvels, it’s an experience filled with awe and learning. However, the magnificence of these structures comes with inherent risks, making safety an abs....

Battery energy storage is a critical technology to reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and build a low carbon future. Renewable energy generation is fundamentally different from traditional fossil fuel energy generation in that energy cannot be p....

Not enough people know that hydrogen fuel cells are a zero-emission energy technology. Even fewer know water vapor's outsized role in electrochemical processes and reactions. Producing electricity through a clean electrochemical process with water....

In the ever-evolving landscape of sustainable transportation, a ground-breaking shift is here: 2024 ushers in a revolutionary change in Electric Vehicle (EV) tax credits in the United States. Under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), a transforma....
Now more than ever, it would be difficult to overstate the importance of the renewable energy industry. Indeed, it seems that few other industries depend as heavily on constant and rapid innovation. This industry, however, is somewhat unique in its e....

University of Toronto’s latest student residence welcomes the future of living with spaces that are warmed by laptops and shower water. In September 2023, one of North America’s largest residential passive homes, Harmony Commons, located....

For decades, demand response (DR) has proven a tried-and-true conservation tactic to mitigate energy usage during peak demand hours. Historically, those peak demand hours were relatively predictable, with increases in demand paralleling commuter and ....